| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: PC Installation. |
| |
Network Configuration
Description: Get turtlebot and your pc chatting to each other.Keywords: turtlebot installation
Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Contents
ROS requires bidirectional networking between all computers attached to the network and does not have security built in. Network for turtlebot and remote pc can be configured with their IP addresses. It can also be done with nameserver or /etc/hosts.
For more information see ROS/NetworkSetup and ROS/EnvironmentVariables
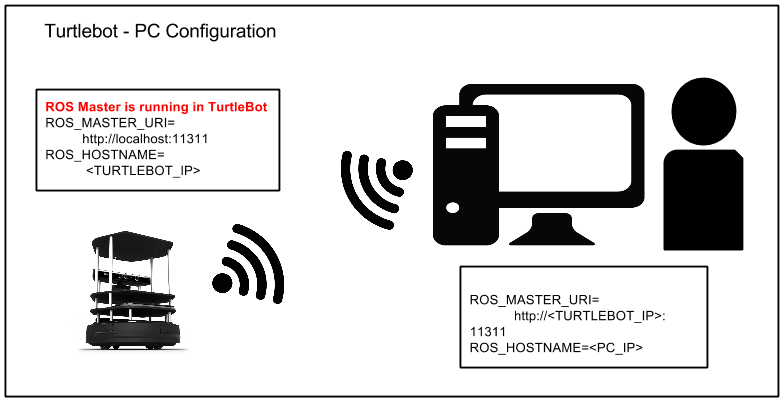
Ultimately you will need to configure ROS_MASTER_URI and ROS_HOSTNAME correctly to ensure the ros communication channels can find each other.
Determining IP addresses
IfConfig
Get the ip addresses of both your turtlebot and the pc (more help) .
To determine a computer's IP address and network interface in linux:
ifconfig
You will see something like:
lo Link encap:Local Loopback inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0 inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1 RX packets:6658055 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:6658055 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:0 RX bytes:587372914 (587.3 MB) TX bytes:587372914 (587.3 MB) wlan1 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 48:5d:60:75:58:90 inet addr:10.0.129.17 Bcast:10.0.129.255 Mask:255.255.254.0 inet6 addr: fe80::4a5d:60ff:fe75:5890/64 Scope:Link UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1 RX packets:101983 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0 TX packets:37244 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0 collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000 RX bytes:49326141 (49.3 MB) TX bytes:7588044 (7.5 MB)the network interface for the wireless card is wlan1
the IP address of the computer is 10.0.129.17
Confirm Connectivity
Ensure that you can ping between machines (more help) .
Ping from the laptop to the workstation and back by IP, or fully resolved hostname. From TurtleBot laptop ping workstation/desktop using IP_OF_WORKSTATION
ping IP_OF_WORKSTATION
Note: Replace IP_OF_TURTLEBOT with actual IP address of TurtleBot that was determined in previous step.
From workstation ping TurtleBot using IP_OF_TURTLEBOT
ping IP_OF_TURTLEBOT
Install an ssh server on Turtlebot.
> sudo apt-get install openssh-server
This is needed for the next tutorial, in which you close the Turtlebot lid and log into it from the remote PC using ssh.
Confirm that you can ssh to Turtlebot from the remote PC.
> ssh turtle@<TURTLEBOTP_IP>
Replace turtle in the command above with the username you created when installing the turtlebot software, and replace <TURTLEBOT_IP> with the hostname or IP address of Turtlebot.
Turtlebot Setup
The instructions differ depending on whether you installs from debs, or from source.
Deb Installation
You should export the variables inside your work space setup script.
> echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://localhost:11311 >> ~/.bashrc > echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=IP_OF_TURTLEBOT >> ~/.bashrc
Finally, bring down turtlebot if you have already launched it and relaunch.
Source Installation
You should export the variables inside your workspace setup script.
> echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://IP_OF_TURTLEBOT:11311 >> ~/turtlebot/devel/setup.sh > echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=IP_OF_TURTLEBOT >> ~/turtlebot/devel/setup.sh
Finally, bring down turtlebot if you have already launched it and relaunch.
Remote PC Setup
You should export the variables inside your workspace setup script. Note that the meaning of the ROS_MASTER_URI changes here - the master is in the turtlebot!
> echo export ROS_MASTER_URI=http://IP_OF_TURTLEBOT:11311 >> ~/.bashrc > echo export ROS_HOSTNAME=IP_OF_PC >> ~/.bashrc
Verification
The following section is not strictly necessary. However, if there is a problem with the ROS networking setup between the TurtleBot and remote pc, it will be easier to identify it early.
Be sure to relaunch turtlebot if you have manually set these variables.
Verify from Remote PC to TurtleBot
Open a new command line terminal on remote pc and run:
> rostopic list
If you don't see list of topics check the value of ROS_MASTER_URI.
On remote pc run:
> rostopic echo /diagnostics
If you don't get a warning that topic has not been published, then verify that ROS_HOSTNAME is set correctly on the TurtleBot laptop.
Verify from TurtleBot to Remote PC
Finally, check that TurtleBot laptop can get data from ROS node running on remote pc.
On remote pc run:
> rostopic pub -r10 /hello std_msgs/String "hello"
On TurtleBot run
> rostopic echo /hello
The message "hello" begin printed about 10 times a second. If not, check the ROS_HOSTNAME setting on the remote pc.
Network Time Protocol
Clock synchronization is important for ROS. Chrony has been found to be the best ntp client over lossy wireless. In case of robot behaves strange when messages are sent from PC application(like rviz, rqt, or ros node running in PC), you need clock synchronization.
- Install Chrony
sudo apt-get install chrony
- manually sync NTP
sudo ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
External references
Network Configuration Tutorial on Gaitech EDU website (includes a video)
What Next?
Bring-up TurtleBot or return to TurtleBot main page.