!
| Note: This tutorial assumes that you have completed the previous tutorials: RGB-D Hand-Held Mapping With a Kinect. |
| |
Wifi Signal Strength Mapping (User Data Usage)
Description: This tutorial shows how to add user data during mapping that will be saved directly in RTAB-Map's database for convenience.Tutorial Level: INTERMEDIATE
Contents
Introduction
Version >0.11.14 required.
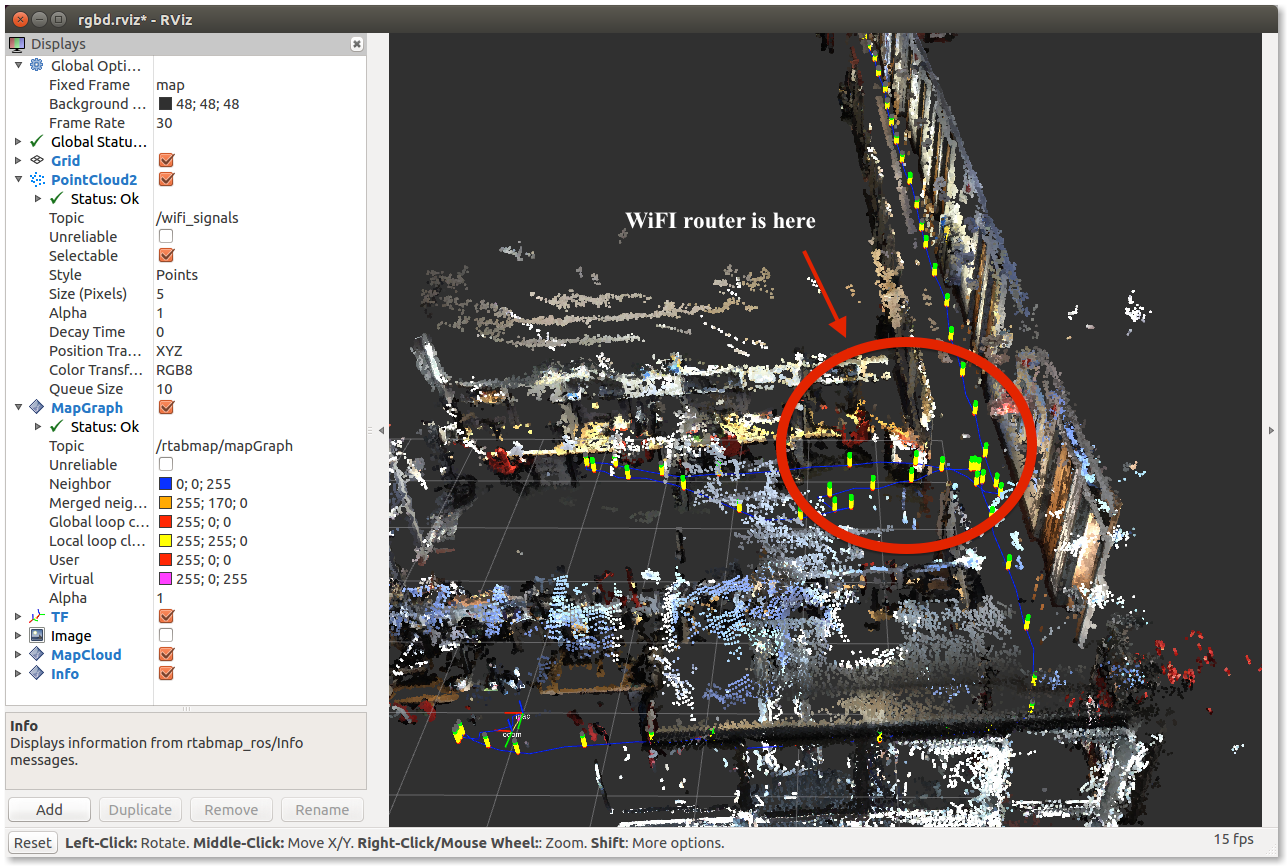
This tutorial will show how to create a map including information taken with any other sensor (e.g., the user data). For convenience, we will map Wifi signal strength of the environment. The screenshot below shows how the Wifi signal strength is visualized. It is just a level bar used (sensor_msgs/Pointcloud2), but more fancy output like Markers can be used to customize the look. 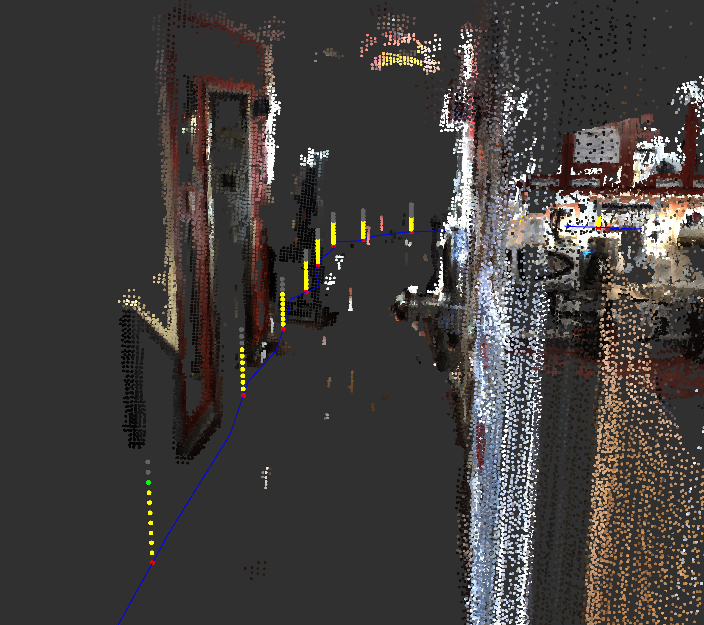
How to Publish User Data (wifi_signal_pub)
To add user data to map, rtabmap node has topics called user_data and user_data_async. The first one is used when parameter subscribe_user_data:=true, and it will be synchronized with other sensor data. It means that the publishing rate of this topic should be high (at least as fast as the images received). The second topic user_data_async is asynchronous. It should be used only when user data is published slower than the detection rate of rtabmap (default 1 Hz). The received user data will be saved in the next node created in rtabmap (if user data is published faster than nodes are created, old user data will be overwritten).
For this example, we use user_data_async with a Wifi signal data published each 2 seconds. Here is the basic information needed to publish a rtabmap_ros/UserData topic (the full code is here):
1 #include <rtabmap_ros/MsgConversion.h>
2 #include <rtabmap_ros/UserData.h>
3
4 int main(int argc, char** argv)
5 {
6 //... node initialization stuff
7
8 ros::Rate rate(0.5);
9
10 ros::Publisher wifiPub = nh.advertise<rtabmap_ros::UserData>("wifi_signal", 1);
11
12 while(ros::ok())
13 {
14 ros::Time stamp = ros::Time::now();
15
16 // Get signal strength...
17 int dBm = ...
18
19 // Create user data [level, stamp].
20 // OpenCV matrix is used for convenience. Any format is accepted.
21 // However, if CV_8UC1 format is used, make sure rows > 1 as
22 // rtabmap will think it is already compressed.
23 cv::Mat data(1, 2, CV_64FC1);
24 data.at<double>(0) = double(dBm);
25
26 // We should set stamp in data to be able to
27 // retrieve it from the saved user data as we need
28 // to get precise position in the graph afterward.
29 data.at<double>(1) = stamp.toSec();
30
31 rtabmap_ros::UserData dataMsg;
32 dataMsg.header.frame_id = "wifi_link";
33 dataMsg.header.stamp = stamp;
34
35 // Convert OpenCV matrix to UserData msg. Optionally,
36 // we can choose to compress the data now (here we keep uncompressed).
37 rtabmap_ros::userDataToROS(data, dataMsg, false);
38
39 // Publish data!
40 wifiPub.publish<rtabmap_ros::UserData>(dataMsg);
41
42 ros::spinOnce();
43 rate.sleep();
44 }
45 return 0;
46 }
Publisher example in Python
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2 import rospy
3 import struct
4 import os
5 from rtabmap_ros.msg import UserData
6
7 def loop():
8 rospy.init_node('wifi_signal_pub', anonymous=True)
9 pub = rospy.Publisher('wifi_signal', UserData, queue_size=10)
10 rate = rospy.Rate(0.5) # 0.5hz
11 while not rospy.is_shutdown():
12
13 myCmd = os.popen('nmcli dev wifi | grep "^*"').read()
14 cmdList = myCmd.split()
15
16 if len(cmdList) > 6:
17 quality = float(cmdList[6])
18 msg = UserData()
19
20 # To make it compatible with c++ sub example, use dBm
21 dBm = quality/2-100
22 rospy.loginfo("Network \"%s\": Quality=%d, %f dBm", cmdList[1], quality, dBm)
23
24 # Create user data [level, stamp].
25 # Any format is accepted.
26 # However, if CV_8UC1 format is used, make sure rows > 1 as
27 # rtabmap will think it is already compressed.
28 msg.rows = 1
29 msg.cols = 2
30 msg.type = 6 # Use OpenCV type (here 6=CV_64FC1): http://ninghang.blogspot.com/2012/11/list-of-mat-type-in-opencv.html
31
32 # We should set stamp in data to be able to
33 # retrieve it from the saved user data as we need
34 # to get precise position in the graph afterward.
35 msg.data = struct.pack(b'dd', dBm, rospy.get_time())
36
37 pub.publish(msg)
38 else:
39 rospy.logerr("Cannot get info from wireless!")
40 rate.sleep()
41
42 if __name__ == '__main__':
43 try:
44 loop()
45 except rospy.ROSInterruptException:
46 pass
How to Retrieve User Data (wifi_signal_sub)
rtabmap publishes rtabmap_ros/MapData topic after each update. In this topic, we can get the user data that we published to rtabmap earlier, which is now linked to graph. Here is an example (the full code is here):
1 #include <rtabmap_ros/MapData.h>
2 #include <rtabmap_ros/MsgConversion.h>
3
4 std::map<double, int> wifiLevels;
5 void mapDataCallback(const rtabmap_ros::MapDataConstPtr & mapDataMsg)
6 {
7 // Convert MapData message in more user friendly objects
8 rtabmap::Transform mapToOdom;
9 std::map<int, rtabmap::Transform> poses;
10 std::multimap<int, rtabmap::Link> links;
11 std::map<int, rtabmap::Signature> signatures;
12
13 rtabmap_ros::mapDataFromROS(*mapDataMsg, poses, links, signatures, mapToOdom);
14
15 // The user data of the latest node added to
16 // map is contained in signatures map. Iterate over
17 // to get the data. Handle the case where we can
18 // receive only latest data, or if all data are published
19 for(std::map<int, rtabmap::Signature>::iterator iter=signatures.begin(); iter!=signatures.end(); ++iter)
20 {
21 int id = iter->first;
22 rtabmap::Signature & node = iter->second;
23
24 if(!node.sensorData().userDataCompressed().empty())
25 {
26 cv::Mat data;
27 node.sensorData().uncompressDataConst(0 ,0, 0, &data);
28
29 if(data.type() == CV_64FC1 && data.rows == 1 && data.cols == 2)
30 {
31 // format [int level, double stamp], see wifi_signal_pub_node.cpp
32 int level = data.at<double>(0);
33 double stamp = data.at<double>(1);
34 wifiLevels.insert(std::make_pair(stamp, level));
35 }
36 else if(!data.empty())
37 {
38 ROS_ERROR("Wrong user data format for wifi signal.");
39 }
40 }
41 }
42
43 // "wifiLevels" contains all signal values sorted
44 // by timestamp. We can then find their exact position
45 // on the graph. See referred source code for details...
46 }
47
48
49
50 int main(int argc, char** argv)
51 {
52 //... node initialization stuff
53
54 ros::Subscriber mapDataSub = nh.subscribe("/rtabmap/mapData", 1, mapDataCallback);
55
56 ros::spin();
57 }
Example of Usage
From the hand-held tutorial, start your camera and launch rtabmap.launch with argument "user_data_async_topic:=/wifi_signal", then start wifi publisher and subscriber:
$ roslaunch rtabmap_ros rtabmap.launch [...] user_data_async_topic:=/wifi_signal // C++: $ rosrun rtabmap_ros wifi_signal_pub _interface:="wlan0" // Python: $ python wifi_signal_pub.py $ rosrun rtabmap_ros wifi_signal_sub
In RVIZ, add PointCloud2 topic called wifi_signals published from wifi_signal_sub node. Note that you may need to start wifi_signal_pub in sudo. To do so:
$ sudo su
$ source /opt/ros/kinetic/setup.bash
$ source /home/{user_name}/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash (if rtabmap is built from source)
$ rosrun rtabmap_ros wifi_signal_pub interface:="wlan0"If you move the camera, you should see the signal strength bars like in the screenshots above.
Example of Result
You can show the map of the screenshots above using this database demo_wifi.db (taken with a stereo camera) with the lines below:
$ roslaunch rtabmap_ros rtabmap.launch database_path:=~/Downloads/demo_wifi.db rtabmapviz:=false rviz:=true $ rosrun rtabmap_ros wifi_signal_sub // In RVIZ, add `PointCloud2` topic called `wifi_signals` $ rosservice call /rtabmap/publish_map 1 1 0







